

BS
Licensed insurance agent

Cake values integrity and transparency. We follow a strict editorial process to provide you with the best content possible. We also may earn commission from purchases made through affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. Learn more in our affiliate disclosure.
One of most people's goals is to have a career that allows them to do what they love. We spend years going to school and often take out considerable student loans to gain an education that will enable us to have a job that leaves us personally fulfilled and financially secure.
But, what if a serious illness or injury prevents you from being able to perform that dream job? Without your paycheck, how will you pay your bills each month? Your rent or mortgage payment, and all of your other debts and obligations, will still be there and need to be paid.
Fortunately, disability insurance provides an income when you can't work. This article will cover everything you need to know about long-term disability insurance, including what it is, how much it pays, when it kicks in, how long it pays, and more.
Jump ahead to these sections:
Read on if you'd like to learn more about protecting your income.
Long-term disability (LTD) insurance is a product offered by many health and life insurance companies that replaces a portion of your income when you can't work because of a severe injury or illness. Insurance companies sell it to businesses and organizations that offer it as an employee benefit or directly to individuals.

The primary difference between these two types of disability insurance is the length of time the insurer will pay benefits.
Short-term disability (STD) insurance policies are designed to replace a portion of your income for a maximum of two years. If your disability was to extend beyond that, the insurer would stop paying you, possibly leaving you without a source of income.
Long-term disability insurance is designed to replace lost income for many years, with some policies paying benefits to age 65 or 67. It covers injuries and illnesses that are potentially permanent, whereas STD policies are geared towards covering temporary disabilities.
For example, a short-term disability insurance policy would benefit a plumber who breaks their arm and can’t work for six weeks, but it won’t help an airline pilot diagnosed with vertigo and will never be able to fly again. LTD insurance would be needed in that case.
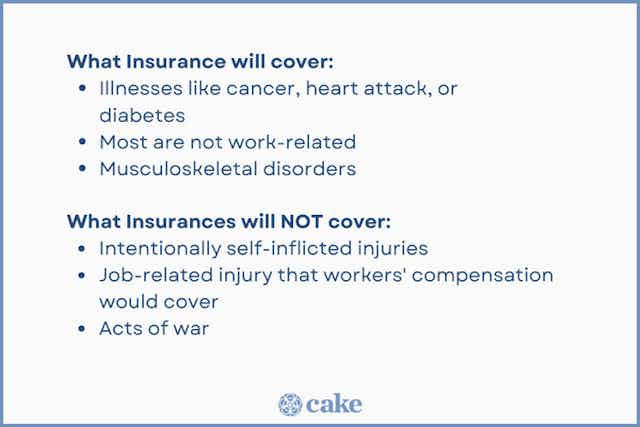
According to the Council for Disability Awareness , the most common causes of disability:
Here is a chart with common terms and examples of disability claims diagnoses.
LTD insurance contains standard exclusions that you’ll find on most life, health, and disability insurance policies:
LTD policies often won’t cover people with other pre-existing conditions like:
To have a claim approved, you need to meet the definition of disability written in your policy. This can vary significantly by policy and insurance company.
The length of time you’ll receive benefits depends on the term you selected when applying for your policy and what’s written in your policy. The benefit period for individual long-term disability insurance is usually 2, 5, or 10 years, or until ages 65 or 67.
The insurance company is obligated to continue to pay you every month for as long as the contract stipulates, unless or until you can return to work, at which point benefit payments will end.
People who buy LTD insurance would not be able to survive financially without a paycheck if they were unable to work because they became disabled due to illness or injury.
For example, an office worker who collects a paycheck every two weeks only if they show up for work will typically buy LTD insurance because their check depends upon their active employment.
But, someone who lives off passive income , like rent from property owned or dividends from stocks in their portfolio, wouldn’t typically buy disability insurance, nor would they qualify. This is because insurance companies only approve applications from people actively engaged in an occupation that generates income.
Many factors influence the cost of an LTD policy. They include personal factors like:
In addition to these personal factors, there are several choices you’ll make when you apply for your policy that will influence what your monthly premium will be:
Benefit period: this is the amount of time that the insurer is obligated to pay you a benefit if you can’t work (2, 5, 10 years, or to age 65 or 67). The longer the insurance company will have to write you a check every month, the higher your premium will be. Most insurance agents recommend a five-year benefit period as the most cost-effective.
Elimination period: also known as the “waiting period,” the elimination period is similar to the deductible on a health insurance policy. Premiums run the opposite of the elimination period you select: the longer you wait for the insurer to begin to pay, the lower your premium will be.
Elimination periods for LTD policies can be as short as 30 days or as long as 365 days. The standard length is 60 or 90 days.
Benefit amounts for LTD policies are based on your income level and the percentage of your income that will be replaced. Policies typically replace anywhere from 60 percent to 80 percent of your gross income.

One of the primary considerations when buying LTD insurance is the insurer’s definition of disability. Policies will typically define disability in one of two ways: any occupation or own occupation.
Any occupation definition means you can't receive benefits if you can do any other job, regardless of its pay. For example, under any occupation definition, a teacher who can't perform their job duties in the classroom but could work as a retail salesperson would not qualify for benefits.
Any occupation is the strictest definition of disability you’ll find. A policy with this definition will have the lowest premiums, but you’ll also get the least coverage.
An own occupation definition of disability is more liberal than any occupation. It defines disability as your inability to work in your profession. The teacher in our example above would qualify for benefits under their own occupation policy by not being able to perform their duties as a teacher, even though they could do something else professionally.
Most own occupation policies also pay benefits if:
As you can tell, a policy’s definition of disability will make a huge difference in what you can potentially receive in benefits. Therefore, be sure to read a sample policy before you complete an application carefully. Not understanding if your policy will be any occupation or your occupation can be a costly mistake.
There are two other features that any LTD insurance policy you buy should have: non-cancelable coverage and residual benefits.
Non-cancelable coverage means the insurance company can never cancel your coverage unless you don’t pay your premiums. Residual benefits stipulate that you’ll receive partial benefits if you can’t perform your duties full-time, but you can perform them on a limited basis.
Other features/riders you should consider:
Cost of living adjustment (COLA) rider: this rider increases your benefit amount by taking inflation into account during a long-term claim.
Future increase option: guarantees your right to buy additional coverage up to a stated age without undergoing medical underwriting again.
Unemployment waiver of premium: policy premiums are waived if you lose your job.
Catastrophic disability benefit: if you become unable to perform two or more activities of daily living (e.g., eating, bathing, dressing, mobility, continence), experience cognitive impairment, or lose sight in both eyes or hearing in both ears, you’ll receive up to 100% of your previous income from all sources.
Do benefits coordinate with other benefits, such as worker’s compensation or Social Security?
This depends on your policy. Some LTD policies will pay out the full benefit regardless of what you receive from Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or worker’s compensation. Others will offset (reduce) your policy’s benefit by the amount you receive from your other sources.
How much coverage should I have?
You should have at least enough coverage to pay your monthly living expenses (mortgage/rent, groceries, utilities, etc.). In addition, most insurers recommend getting benefits equal to 60% of your pre-tax salary.
Should you get an individual disability insurance policy if you have group disability coverage?
Even if you have LTD insurance coverage through work, most financial advisors recommend that you consider purchasing an individual policy. The main reason is that if you leave your employer, you probably won’t be able to take your coverage with you, and if your health has changed for the worse, you probably won’t qualify for an individual policy.
Also, your group LTD insurance policy’s monthly benefit might not be enough to cover all of your monthly expenses, particularly if your policy has a cap on coverage.
When is the right time to purchase disability insurance?
The best time to purchase any type of insurance is when you’re younger and healthier. Insurance premiums rise with age, and there’s no guarantee you’ll be able to qualify medically in the future.
Should I get long-term disability insurance?
If you earn an income, you should seriously consider buying LTD insurance, especially if:
A Final Thought
If you’re considering buying long-term disability insurance as an individual or through your employer, don’t delay making your decision. A serious accident or injury can occur any time, anywhere. The worst thing you can do is to assume that “It won’t happen to me.”